Verification of Payee Architecture: Cloud-Native vs On-Premise Approaches
Why VoP Architecture Decisions Shape Your Payment Future
VoP implementation forces architectural decisions that will shape your payment infrastructure for years. The choice between cloud-native, on-premise, or hybrid deployment isn’t just about technology preferences — it’s about operational constraints, regulatory requirements, and long-term scalability.
Major European banks are split. Some are betting on cloud scalability, others are doubling down on on-premise control. Most are discovering that their existing infrastructure assumptions don’t align with VoP performance requirements.
Understanding these architectural trade-offs becomes critical as the October 2025 VoP deadline approaches and payment systems require reliable, compliant verification infrastructure.
Architecture Comparison: Key Trade-offs
| Aspect | Cloud-Native | On-Premise |
|---|---|---|
| ✅ Pros | • Automatic scaling and elasticity | • Complete control over data and infrastructure |
| • Fast integration and DevOps approach | • Compliance with internal policies and certifications | |
| • Quick deployment (no hardware procurement) | • Seamless integration with existing legacy systems | |
| • Built-in redundancy and disaster recovery | • Predictable performance without external dependencies | |
| • Lower operational overhead | • No vendor lock-in concerns | |
| 🔻 Cons | • Potential vendor lock-in | • High upfront capital investment |
| • Dependency on external infrastructure | • Limited scalability during traffic spikes | |
| • GDPR/Data residency compliance challenges | • Longer time-to-market | |
| • Variable long-term costs | • Higher operational overhead and expertise requirements | |
| • External service dependencies | • Manual capacity planning required |
The Architecture Decision Matrix
When evaluating VoP deployment options, three factors drive most architectural decisions:
Performance Requirements: SEPA Instant’s 10-second transaction limits mean VoP latency directly impacts compliance. Your architecture must consistently deliver sub-2-second verification responses under peak load conditions.
Regulatory Constraints: Data sovereignty, audit trail requirements, and compliance frameworks often dictate where VoP infrastructure can be deployed and how it must be managed.
Operational Capacity: Internal DevOps capabilities, existing infrastructure investments, and long-term maintenance resources influence which deployment models are sustainable for your organization.
Cloud-Native VoP: The Scalability Play
Performance and Elasticity
Cloud-native VoP solutions handle traffic spikes without pre-provisioned capacity. During peak payment hours — typically 9-11 AM and 2-4 PM in European markets — transaction volumes can increase several hundred percent above baseline. Cloud infrastructure scales automatically.
In practice, European PSPs report that seasonal traffic spikes often exceed static capacity planning by significant margins. Cloud infrastructure handles these load patterns without manual intervention or performance degradation.
Latency Considerations: Modern cloud regions provide sub-10ms latency for intra-European VoP requests. Edge computing and CDN integration can reduce response times below traditional data center deployments.
Development and Integration Speed
Cloud-native platforms offer API-first architectures that accelerate integration. Development teams can prototype, test, and deploy VoP functionality faster than traditional infrastructure approaches.
# Example cloud-native VoP deployment configuration
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: vop-service
spec:
replicas: 3
template:
spec:
containers:
- name: vop-api
image: checkpayee/vop-service:latest
resources:
requests:
memory: "256Mi"
cpu: "250m"
limits:
memory: "512Mi"
cpu: "500m"
env:
- name: VOP_REGION
value: "eu-west-1"
- name: SCALING_TARGET
value: "1000ms"DevOps Advantages:
- Automated scaling based on transaction volume patterns
- Rolling updates without payment processing downtime
- Multi-region deployment for redundancy and performance
- Integrated monitoring with real-time performance analytics
Integration Reality: Cloud platforms provide pre-built connectors for major payment processors, reducing custom integration work. But legacy bank systems often require custom middleware regardless of deployment model.
Operational Overhead
Cloud deployment shifts operational burden from internal IT teams to managed service providers. This reduces infrastructure management overhead but creates dependency on external platforms.
Cost Structure: Cloud pricing scales with usage, making it attractive for growing PSPs. But high-volume institutions may face higher long-term costs compared to amortized on-premise infrastructure.
On-Premise VoP: The Control Imperative
Data Sovereignty and Compliance
Many European banks require on-premise deployment for regulatory compliance and data sovereignty. GDPR, national banking regulations, and internal risk policies often mandate local data processing and storage.
Regulatory Drivers:
- Data residency requirements for customer payment information
- Audit trail controls for regulatory examination access
- Security certification processes favoring on-premise deployment
- Change management procedures requiring internal infrastructure control
Compliance Reality: Many banks have discovered that cloud deployment requires extensive compliance review processes that can delay implementation significantly, particularly when working against regulatory deadlines.
Integration with Legacy Systems
Large banks operate payment infrastructure built over decades. Core banking systems, fraud monitoring platforms, and settlement networks often require on-premise integration for performance and security reasons.
Legacy Considerations:
- Network latency between cloud VoP and on-premise payment processing
- Security protocols that don’t support cloud-to-premise data flows
- Change approval processes that resist external dependencies
- Technical debt in existing systems that complicate cloud integration
Common integration challenges include latency issues between cloud-based VoP services and legacy mainframe payment processors. These typically require dedicated network infrastructure and custom caching layers to resolve, often adding months to implementation timelines.
Performance Predictability
On-premise deployment provides consistent, predictable performance without external network dependencies. This matters for banks with strict SLA requirements and low tolerance for third-party service disruptions.
# Example on-premise VoP performance monitoring
# Custom metrics for internal infrastructure
vop_response_time_p95{environment="production"} 980
vop_throughput_per_second{region="eu"} 1200
vop_cache_hit_ratio{service="name_verification"} 0.85
vop_database_connections{pool="primary"} 45Control Advantages:
- Dedicated infrastructure without noisy neighbor effects
- Network optimization for specific payment processing requirements
- Security hardening aligned with internal standards
- Capacity planning based on known usage patterns
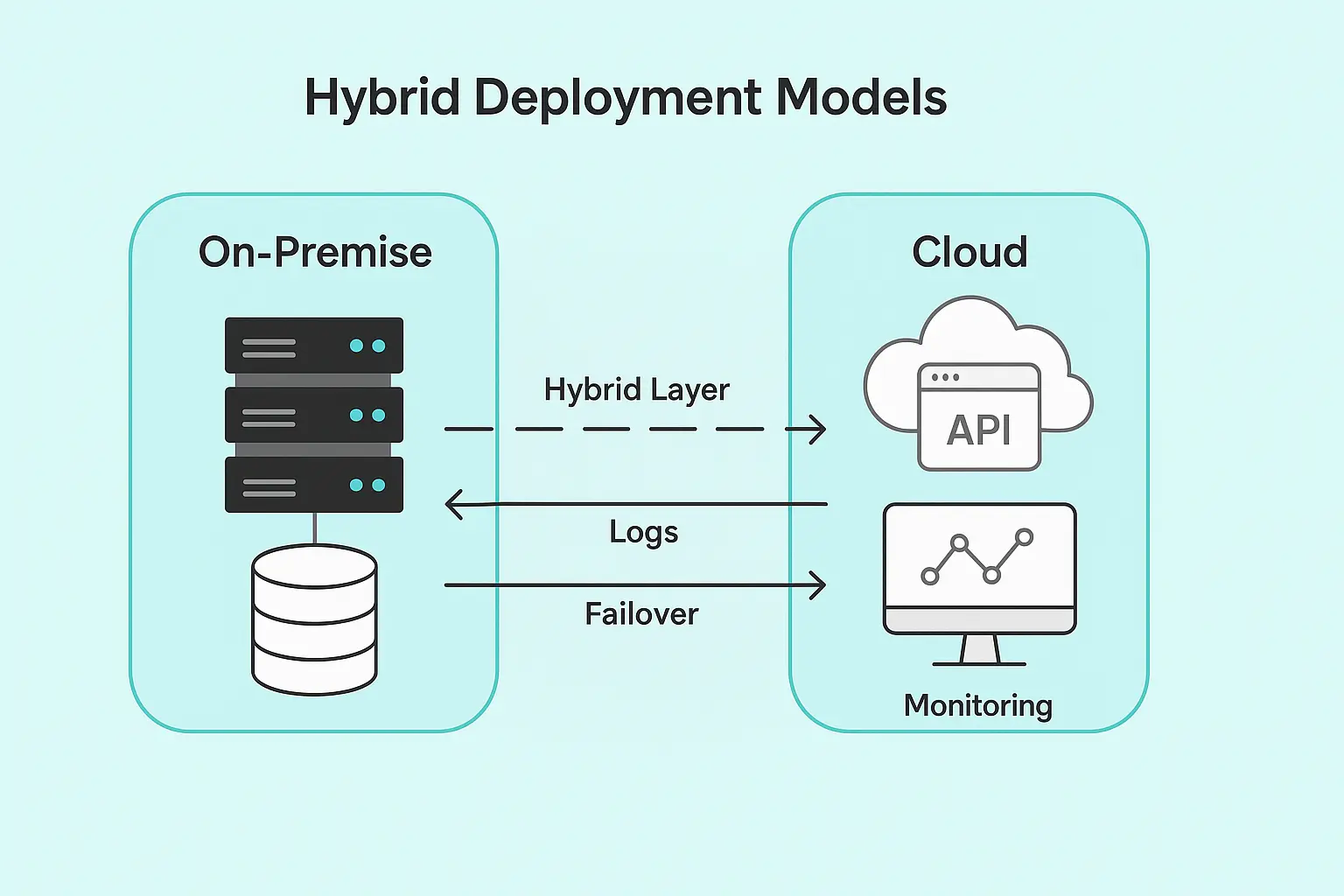
Hybrid Approaches: Balancing Trade-offs
Strategic Deployment Models
Many large institutions adopt hybrid approaches that balance cloud scalability with on-premise control. Common patterns include:
Primary/Secondary Architecture: On-premise VoP processing with cloud failover for business continuity and overflow capacity.
Geographical Distribution: On-premise processing for domestic payments, cloud processing for cross-border transactions requiring geographic distribution.
Service Segregation: Core VoP verification on-premise, reporting and analytics in the cloud for flexibility and cost optimization.
Implementation Complexity
Hybrid deployment requires sophisticated orchestration between on-premise and cloud components. This increases architectural complexity but provides operational flexibility.
Technical Requirements:
- API gateway management across deployment environments
- Data synchronization between on-premise and cloud systems
- Security coordination for cross-environment communication
- Monitoring integration providing unified operational visibility
Implementation Reality: Hybrid complexity often exceeds initial estimates. Organizations frequently report that hybrid VoP implementations require substantially more development effort than anticipated due to cross-environment integration challenges.
Technical Architecture Deep Dive
API Design and Performance
VoP APIs must deliver sub-2-second response times regardless of deployment model. This requires careful attention to:
Database Design: Name matching algorithms need optimized data structures and indexing strategies. Traditional relational databases often struggle with fuzzy matching at scale.
-- Example optimized VoP database schema
CREATE TABLE payee_verification (
id BIGSERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
iban VARCHAR(34) NOT NULL,
payee_name VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
payee_name_normalized VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
verification_result VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL,
confidence_score DECIMAL(3,2),
created_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT NOW()
);
CREATE INDEX idx_payee_iban ON payee_verification(iban);
CREATE INDEX idx_payee_name_normalized ON payee_verification(payee_name_normalized);
CREATE INDEX idx_verification_timestamp ON payee_verification(created_at);Caching Strategies: Frequently requested name verifications benefit from intelligent caching, but cache invalidation must account for account holder updates.
Connection Pooling: Database connection management becomes critical under high VoP request volumes.
Security Architecture
Both cloud and on-premise deployments require robust security, but implementation approaches differ significantly.
Cloud Security:
- Identity and access management through cloud provider IAM systems
- Network segmentation using virtual private clouds and security groups
- Encryption in transit between cloud regions and availability zones
- Compliance certification leveraging cloud provider frameworks
On-Premise Security:
- Network isolation through physical or virtual segmentation
- Access controls integrated with existing directory services
- Hardware security modules for cryptographic key management
- Physical security controls for data center access
Monitoring and Observability
VoP systems require comprehensive monitoring regardless of deployment model. For detailed guidance on implementing production-grade VoP monitoring, see our complete 👉 VoP Monitoring Guide.
Key Metrics to Track:
- Response time distribution for VoP requests
- Success/failure rates by request type
- Queue depth and processing latency
- Database query performance and optimization
Cost Analysis: Total Ownership Considerations
Cloud Economics
Cloud deployment shifts capital expenditure to operational expenditure with usage-based pricing models.
Cost Components:
- Infrastructure costs scaling with transaction volume
- Data transfer charges for cross-region processing
- Managed service fees for platform capabilities
- Integration costs for API management and monitoring
Economic Reality: Cloud costs require understanding actual usage patterns for accurate long-term planning. Initial cost estimates frequently underestimate data transfer and integration expenses that become apparent during production deployment.
On-Premise Investment
On-premise deployment requires significant upfront capital investment but provides long-term cost predictability.
Investment Areas:
- Hardware infrastructure for processing and storage
- Software licensing for databases and middleware
- Operational staff for system administration and maintenance
- Facility costs for data center space and power
Hidden Costs: On-premise deployments accumulate operational overhead that’s often underestimated. Patch management, backup procedures, and disaster recovery planning require dedicated resources.
Decision Framework: Choosing Your Approach
Organizational Readiness Assessment
Cloud-Native Readiness:
- DevOps culture and automation capabilities
- Comfort with external service dependencies
- Regulatory approval for cloud deployment
- Traffic patterns benefiting from elastic scaling
On-Premise Readiness:
- Internal infrastructure and operational expertise
- Regulatory requirements for data sovereignty
- Integration needs with legacy systems
- Predictable capacity and performance requirements
Risk Tolerance Evaluation
Cloud Risks:
- External service dependencies and potential outages
- Data sovereignty and regulatory compliance
- Vendor lock-in and long-term cost predictability
- Integration complexity with existing systems
On-Premise Risks:
- Internal operational overhead and expertise requirements
- Capital investment and long-term cost commitments
- Scalability limitations during traffic spikes
- Disaster recovery and business continuity planning
Implementation Timeline Considerations
Cloud Deployment Advantages
Cloud-native solutions typically reduce implementation timelines through:
- Pre-built infrastructure and platform services
- Automated deployment and configuration tools
- Reduced procurement and approval cycles
- Faster development and testing cycles
On-Premise Implementation Complexity
On-premise deployments require longer timelines for:
- Hardware procurement and data center preparation
- Security certification and compliance approval
- Integration testing with existing systems
- Staff training and operational procedure development
Timeline Reality: The October 2025 VoP deadline influences architectural decisions. Banks with tight timelines often choose cloud deployment to accelerate implementation, then evaluate migration to on-premise for long-term operations.
Future-Proofing Your VoP Architecture
Evolving Regulatory Requirements
VoP regulations will evolve beyond October 2025. Architectural decisions should accommodate:
- Enhanced verification requirements and fraud detection
- Cross-border verification coordination
- Integration with emerging payment technologies
- Expanded reporting and audit capabilities
Technology Evolution
Payment infrastructure continues evolving rapidly. VoP architecture should support:
- API evolution and versioning strategies
- Integration with artificial intelligence and machine learning
- Real-time fraud detection and risk assessment
- Open banking and PSD3 compatibility
Strategic Reality Check
The most successful VoP implementations will be those that balance immediate compliance requirements with long-term architectural flexibility. Neither pure cloud nor pure on-premise approaches provide optimal solutions for all institutions.
Your architectural choice should align with:
- Regulatory constraints specific to your jurisdiction and institution type
- Operational capabilities of your current DevOps and infrastructure teams
- Integration requirements with existing payment processing systems
- Performance expectations for transaction throughput and latency
- Cost optimization goals for both short-term implementation and long-term operations
The key is choosing an approach that meets your immediate VoP compliance needs while providing a foundation for future payment infrastructure evolution.
Need help designing your VoP architecture strategy?
CheckPayee provides VoP solutions that adapt to your architectural requirements. Whether you need cloud-native scalability, on-premise control, or hybrid flexibility, our platform delivers consistent performance and compliance across deployment models.
Contact us to discuss your VoP architectural requirements and deployment timeline.